


Work is on ! Rolls-Royce Tempest engine 'TDV3/1' undergoing intake Integration testing in the TP141 testbed in Filton, Bristol , many other developments , including an ejection seat trials at speeds exceeding 500mph is keeping the partners of Next Gen Stealth Combat aircraft - "Tempest" Busy at different locations.
Latest update from BAE Systems sums up the development as "a new power plant manufacturing process", "a new bespoke simulator" , "high speed ejection seat trials" and "auto-coding software" are under progress as of this day.
Understandably, the “new flying combat air demonstrator” will be essential for the U.K.’s Future Combat Air System (FCAS) as the combat demonstrator will “play a critical role in proving the technology and design principles” for the FCAS.
Inline to this goal, Experts from BAE Systems, Rolls-Royce, Leonardo UK, MBDA and the Ministry of Defence (MOD) are collaborating with a range of British small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs) to develop the technologies needed to deliver the UK’s next generation supersonic stealth combat aircraft, Tempest.
The Flying Technology Demonstrator, first announced by the UK Government in July 2022, is set to fly within the next four years and is being designed using a range of innovative digital techniques and transformative processes, combined with the expertise of the UK’s world-class defence industry.
Although the United Kingdom has access and flies the fifth-generation stealth fighter F-35, the NATO Ally has its own ambitions, and is keen to diversify its air forces by building its own indigenous advanced stealth fighter.
At a brand new facility, at BAE Systems in Warton, Lancashire, test pilots from BAE Systems, Rolls-Royce and the Royal Air Force (RAF) have already flown more than 150 hours of the demonstrator aircraft in a new bespoke simulator, providing crucial evidence to support flight trials.
In a first for military aircraft design, BAE Systems’ engineers have used auto coding to create safety-critical systems software in a matter of days rather than weeks. This enables rapid assessment of the flight control systems during more complex flight manoeuvres with the simulator capturing crucial data about how the jet will handle and perform, years before its first flight.
Engineers have also been carrying out aerodynamic engine testing, harnessing new advanced manufacturing processes to produce an engine duct which is uniquely shaped to slow the air from supersonic to sub-sonic speeds at the engine face.
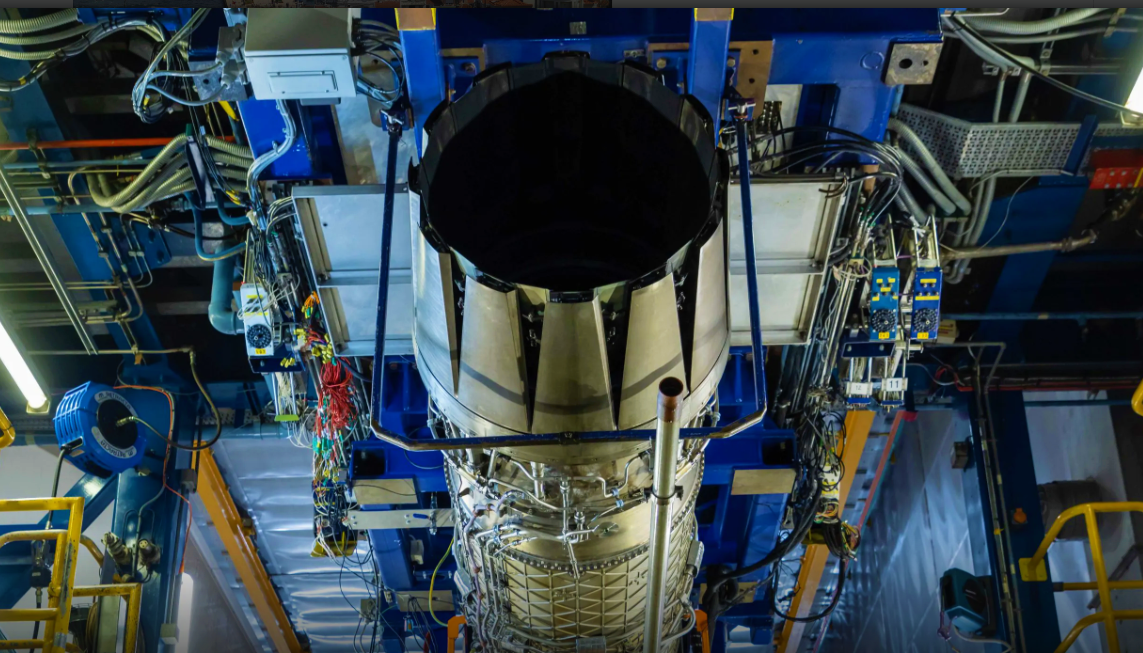
The intake has fewer moving parts than a traditional fighter jet design, enhancing the aircraft's stealthy design. The test was conducted at Rolls-Royce’s site in Filton, Bristol, in the same facility where the Concorde Olympus engine was tested in the 1960s.
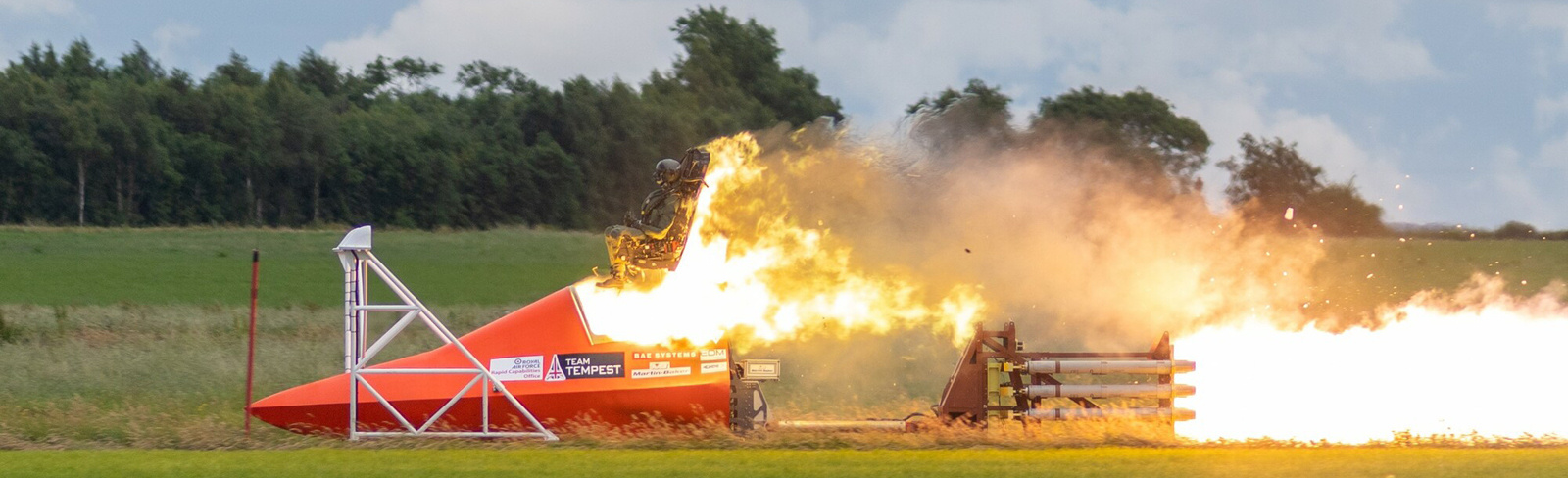
Working alongside UK crew escape specialist, Martin Baker, a team of BAE Systems engineers has led ejection seat trials, using a rocket-propelled sled travelling at speeds of more than 500mph. Experienced engineers have worked alongside junior team members to pass on vital skills which can be taken forward into future developments of Tempest.
This range of novel technologies will demonstrate and test key elements of the next generation combat air design as well as skills, tools, processes and techniques needed to develop Tempest, the aircraft that will be delivered through the Global Combat Air Programme, with the UK, Italy and Japan.
"The Flying Demonstrator programme is a remarkable effort to design and build a supersonic stealth jet that will prove integration and develop our national skills, while providing data and learning in support of Tempest entering service by 2035. Today, for the first time, we are able to lift the lid on some of the key work that is taking place on this important programme. Tempest is no longer just an idea or concept on a computer; our industry partners have made real, tangible progress and are bringing the programme to life through innovative projects, such as the flying demonstrator."
Richard Berthon, Director Future Combat Air for the MOD
"It’s now 40 years since our people led the demonstrator aircraft programme which gave birth to Typhoon and the work we’re doing today is another once-in-a-generation opportunity to write the next chapter in aviation history. Right across the Tempest programme we’re using digital techniques and innovative design and engineering methods, to ensure we can deliver Tempest in service by 2035. "
"We already have 1,000 people involved in this programme across UK industry and the supply chain, with young apprentices and graduates working alongside some of our most experienced engineers. This work will continue to act as a beacon, attracting the very best talent and experience to pass on to future generations of engineers needed for the UK to remain an industry leader in defence and aerospace capability. "
Neil Strang, Tempest Programme Director, BAE Systems
.jpg)
"The aerodynamic testing has been invaluable in several ways. Not only has it validated complex digital techniques and models, but it has fostered highly collaborative working practices between the BAE Systems and Rolls-Royce teams. We have been delighted with the results and now move forward with confidence that together we can deliver on the next stage of the Flying Demonstrator development. "
Conrad Banks, Chief Engineer, Rolls-Royce Defence Future Programmes
In July 2022, Ben Wallace, Secretary of State for Defence, announced plans for a new combat air demonstrator to fly within five years. Speaking at the time, he said:
"The design and development of the demonstrator aircraft represents an important milestone, showcasing the success and talent of our engineers, programmers and software developers."
Focusing on the development of advanced defence electronics, Leonardo is also a founding partner of Team Tempest, alongside the UK MOD, BAE Systems, Rolls Royce and MBDA UK. The team has been working at pace to develop the technologies and capabilities necessary to see a new combat air system go into service in 2035.
Earlier in July 2021, the UK MOD awarded Team Tempest a further contract worth approximately £250m to progress the development of the future capability.
Source and Credit : BAE Systems
Related News......
