


Understanding - An aircraft carrying out take off at engine takeoff thrust level less than the maximum takeoff thrust as per the provisions of Airplane Flight Manual (AFM).
A derated thrust takeoff is a takeoff that is accomplished utilising less thrust than the engines are capable of producing (thrust rating) under the existing conditions of temperature and pressure altitude.
For those asking about this A350 test bed video. It appears to be a de-rated take-off to achieve the minimum screen height on departure. Less noise, less fuel; the 787 does something similar I think. You still have power available if needed. #Airbus #A350 pic.twitter.com/wXElbMhiqs
— Scott Bateman MBE ???? (@scottiebateman) March 28, 2021
- Engine reliability
- Less maintenance
- Improved operating costs.
- Takeoff weight flexibility for a specific runways.
Takeoff operations conducted at thrust (power) settings less than the maximum takeoff thrust (power) available may provide substantial benefits in terms of engine reliability, maintenance, and operating costs.
To meet the Regulatory requirements for takeoff, Operating Manual limitations , altitude , the runway length, parameters factored against the actual aircraft weight and existing environmental conditions are vital for the calculation of the actual amount of thrust necessary for take off.
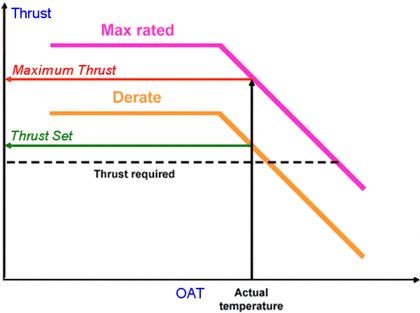
Let’s understand the flat thrust rating of a turbine engine to understand the derated thrust calculations !
► The limitations of a jet engine are the maximum internal pressure that the casing can withstand and the maximum allowable operating temperature.
► Lower altitudes and cooler outside air temperatures (OAT), contribute to the engine capability of producing more pressure and, consequently, more thrust than the engine can contain.
► Here comes FADEC (Full Authority Digital Engine Control), programming of which calculates the flat rate the engine at a thrust setting corresponding to a safe internal engine pressure and this thrust value is the rated or maximum thrust that the engine will produce.
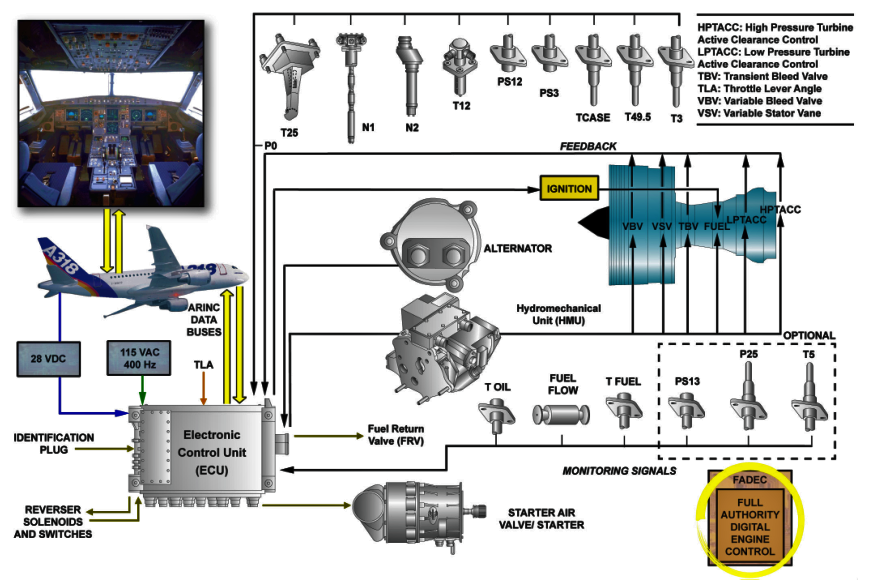
Image Source - Airbus .
► OEM ( Original equipment manufacturers) flat rate the engines by the reference of a specific environmental limit or flat rated temperature that is expressed as an ISA and OAT value or below, at which the engine is capable of producing certain rated thrust.
► The FADEC compensates for varying OAT and presure altitude by adjusting fuel flow and limiting the rotational speed of the engine.
We have two options here ! reduction of engine thrust accurately can be done either by a
Depending on the engine OEM / manufacturer, one or both of these thrust reduction methods may be available for the engine.
► Discussions on FLEX will be save for some other day !
► Basically , we are setting a new Maximum thrust limit !
► A derate selection electronically reduces the the rated thrust of the engine to either one or more prespecified values or by a allowing a percentage of the normal flat rated thrust.
► As this new thrust limit cannot be exceeded during the takeoff phase, critical speeds such as VMCG and VMCA change from those associated with full rated thrust.
► Here,the fixed derate is considered a limitation for takeoff. Takeoff speeds consider ground (VMCG) and in-air (VMCA ) minimum control speeds at the fixed derate level of thrust.
► Thrust levers should not be advanced beyond the fixed derate limit unless conditions are encountered during the takeoff where additional thrust is needed on both engines, such as windshear.
► Operating manual must have performance data for all permissible derate selections.
Derated thrust takeoff results in a slower acceleration on the runway, a longer takeoff roll and a reduced initial climb rate.

► Flight management system (FMS) awaits Pilot entries, risks associated with a derated thrust takeoff are the potential of miscalculations and entering incorrect values into the aircraft FMS.
► These errors could result in the engines producing less / insufficient thrust to safely carry out the takeoff.
► Cross checking of independent calculations by both the pilots should help in obtaining the accuracy.
► A wroungly executed derated thrust takeoff can eventually lead you with runway excursion incidents / accidents and rejected takeoffs (RTO).
Display Image - Airbus .
